The Sun: Our Life-Giving Star
The Sun: Our Life-Giving Star

The Sun is the heart of our solar system, a magnificent sphere of plasma that has been burning for approximately 4.6 billion years. Without the Sun's energy, life as we know it would not exist on Earth.
The Power of the Sun
At the core of the Sun, nuclear fusion reactions transform hydrogen into helium, releasing enormous amounts of energy in the process. This energy radiates outward, traveling 150 million kilometers through space to reach Earth in just over eight minutes. The light and heat we receive from the Sun power virtually all processes on our planet.
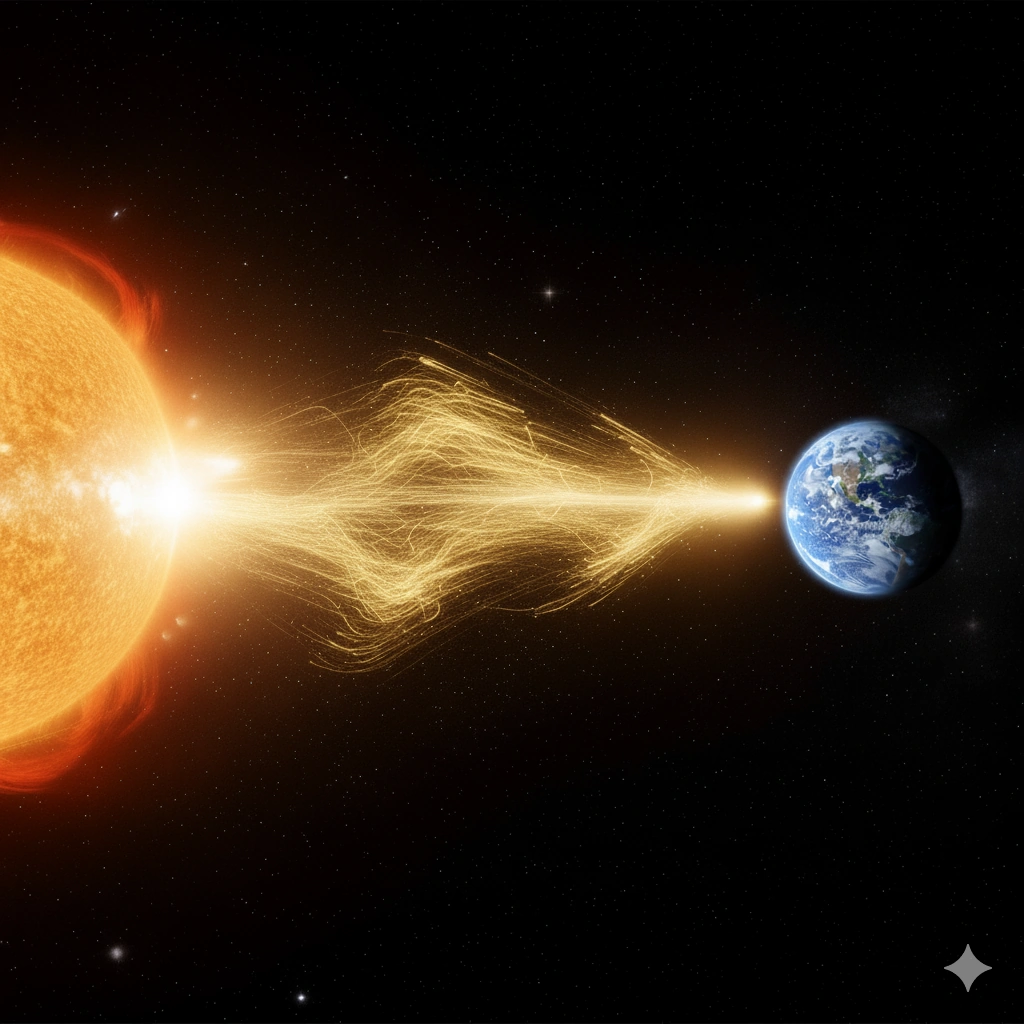

Solar Energy and Life
The Sun's energy is the foundation of almost all life on Earth. Through the process of photosynthesis, plants transform sunlight into chemical energy, producing oxygen as a byproduct. This oxygen sustains animal life, while the plants themselves form the base of the food chain. The Sun's heat also regulates Earth's climate and drives the water cycle, creating the conditions necessary for life to flourish.

The Daily Journey
Each day, the Sun appears to rise in the east and set in the west, a phenomenon caused by Earth's rotation on its axis. This daily cycle has been the most fundamental measure of time throughout human history. The Sun's position in the sky determines the length of day and night, which varies throughout the year due to Earth's tilted axis.
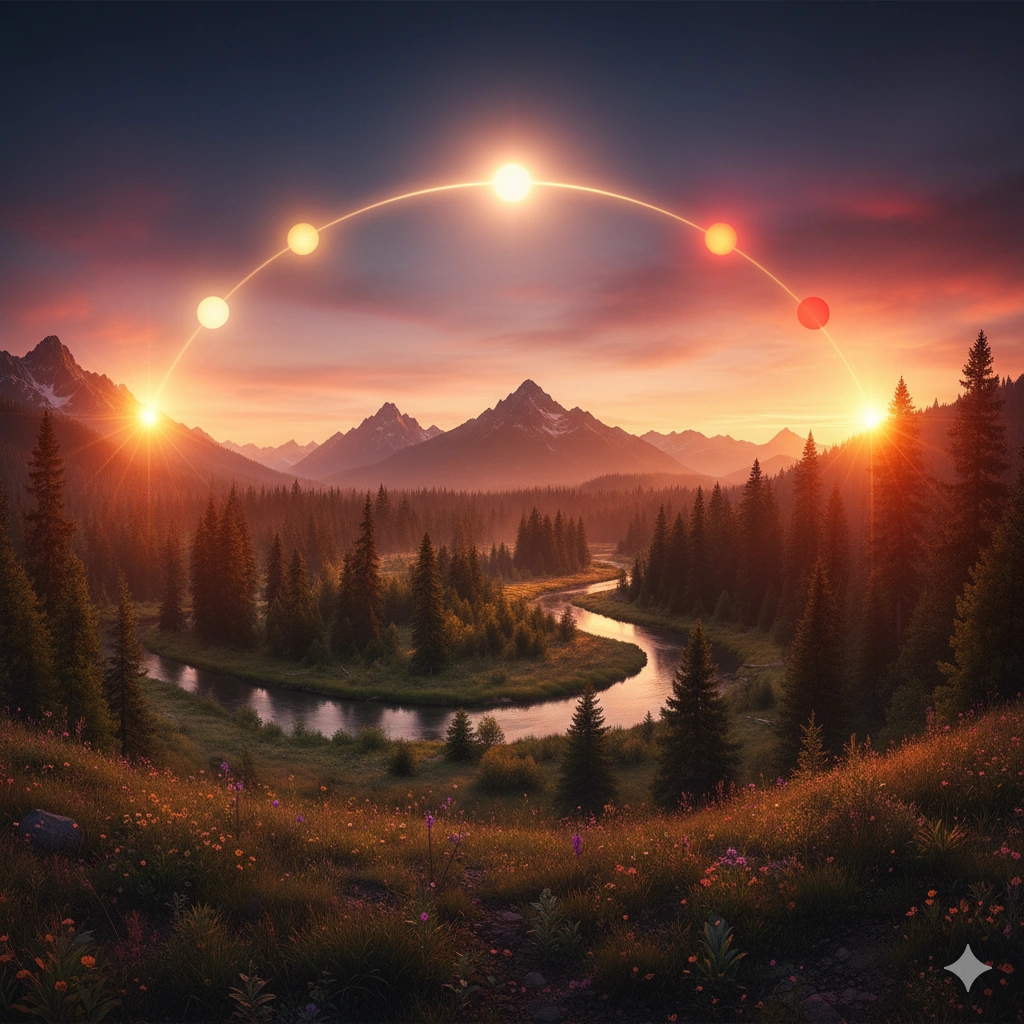

Seasonal Changes
As Earth orbits the Sun over the course of a year, the tilt of our planet's axis causes the changing of the seasons. During summer, the Sun's rays strike more directly, bringing warmth and long days. In winter, the Sun's path is lower in the sky, resulting in shorter days and cooler temperatures. This annual cycle has shaped the evolution of life on Earth and the development of human civilizations.

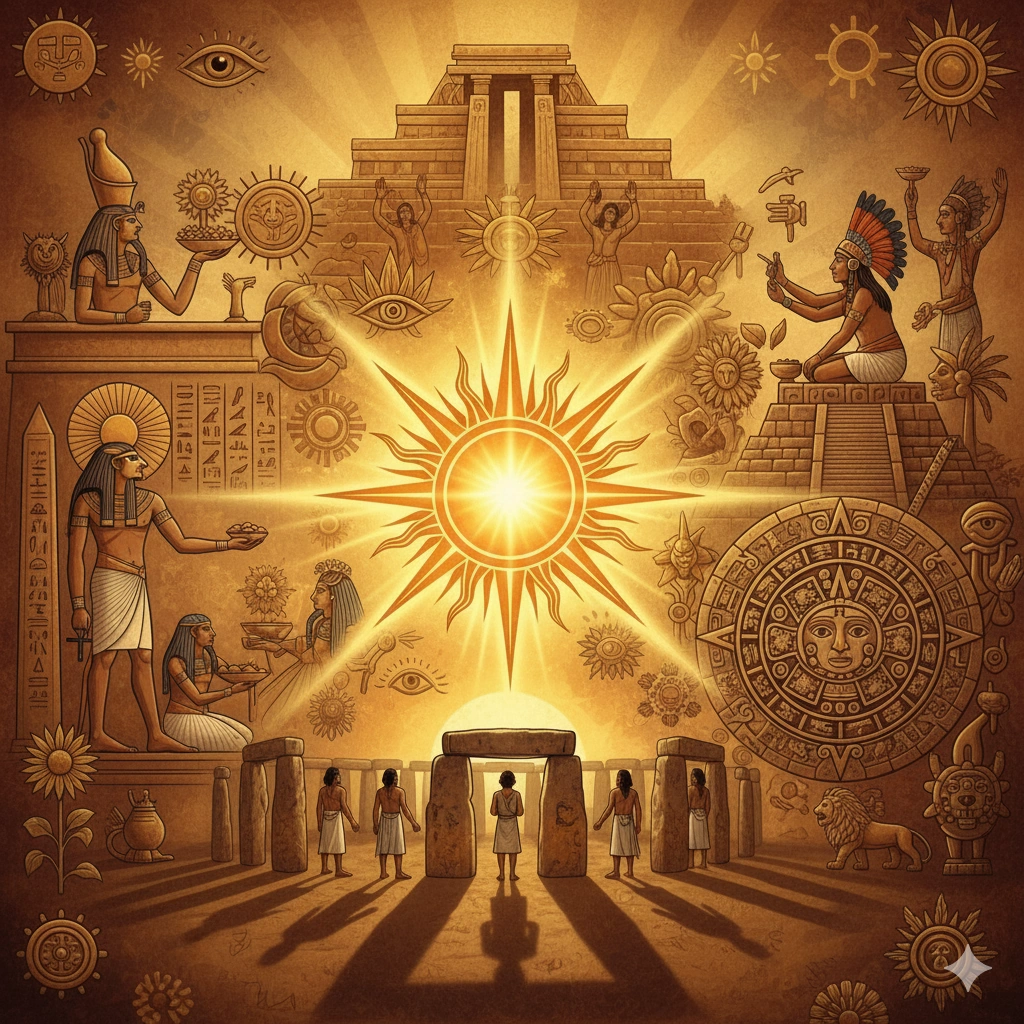
The Sun in Culture
Throughout history, the Sun has been revered as a deity in countless cultures. The ancient Egyptians worshipped Ra, the sun god, while the Aztecs honored Tonatiuh. In many traditions, the Sun represents masculine energy, power, consciousness, and divine light of knowledge. Solar festivals marking the solstices and equinoxes are celebrated worldwide, recognizing the Sun's vital role in the cycle of life.

Solar Symbolism
The Sun symbolizes:
- Life and vitality - The source of all energy
- Consciousness and awareness - Illuminating the world
- Power and authority - The master of the day
- Truth and clarity - Revealing what is hidden
- Growth and abundance - Nourishing all living things
The Sun's Influence on Nature
The Sun's energy powers Earth's weather systems, creating winds, rain, and storms. Ocean currents are influenced by solar heating, which in turn affects global climate patterns. Many animals use the Sun for navigation, while others regulate their biological rhythms according to the daily cycle of light and darkness.

The Sun does not shine for a few trees and flowers, but for the joy of the vast world. — Henry Ward Beecher